Leave Your Message
When it comes to optimizing thermal efficiency in industrial processes, choosing the right Plate To Plate Heat Exchanger is crucial for your business. These devices are renowned for their ability to transfer heat between two fluids efficiently, making them ideal for a wide range of applications, from food processing to HVAC systems. However, with numerous options available on the market, selecting the most suitable heat exchanger can be daunting. This ultimate guide will walk you through the key factors to consider when choosing a Plate To Plate Heat Exchanger, ensuring you make an informed decision that aligns with your operational needs and optimizes energy usage. Whether you're a seasoned professional or new to the industry, understanding the intricacies of these systems will empower you to enhance your processes and achieve better results.
When it comes to plate to plate heat exchangers, understanding their fundamental operation is essential for their effective application in various industries. These systems are engineered to transfer heat between two fluids seamlessly, maximizing energy efficiency without direct contact. The thermophysical properties of the fluids involved play a critical role in determining the effectiveness of the heat exchange process. Recent advancements in heat transfer technologies emphasize the importance of selecting the right materials and configurations, which can significantly impact the performance of these exchangers.
Incorporating innovations such as nanofluids in heat exchangers can enhance their efficiency. Nanofluids, with their superior thermal conductivity, offer promising advantages in applications ranging from industrial plants to renewable energy systems, such as solar collectors. Additionally, the growing concern for energy efficiency and sustainability has prompted the exploration of alternative materials like thermally conductive composites, which can help mitigate issues like corrosion and fouling, ensuring a longer operational life and reduced maintenance costs. Understanding these basic principles is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their thermal management systems and contribute to a more sustainable future.
When it comes to plate to plate heat exchangers, understanding the key types and their applications is crucial for making an informed decision. The most common types include gasketed plate heat exchangers, brazed plate heat exchangers, and welded plate heat exchangers. Gasketed units are known for their flexibility and ease of maintenance, making them suitable for industries like food processing where regulations are strict. In contrast, brazed units are ideal for systems requiring high pressure and temperature conditions, such as in HVAC and refrigeration applications. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global plate heat exchanger market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.4% from 2021 to 2028, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient systems.
When choosing the right type for your business, consider the specific application and fluid properties. For example, welding plates can be beneficial when working with high-temperature fluids, as they provide a robust solution without the risk of gasket degradation. Additionally, think about the maintenance costs and access—gasketed options offer easier servicing, which can reduce downtime in production environments.
Tip: Always consider the thermal efficiency when selecting a heat exchanger type. A higher thermal efficiency can lead to significant energy savings over time. Furthermore, conducting a thorough analysis of your system’s flow rates and pressure drops will help ensure that you choose a heat exchanger that meets your operational requirements without oversizing, which can lead to higher costs.
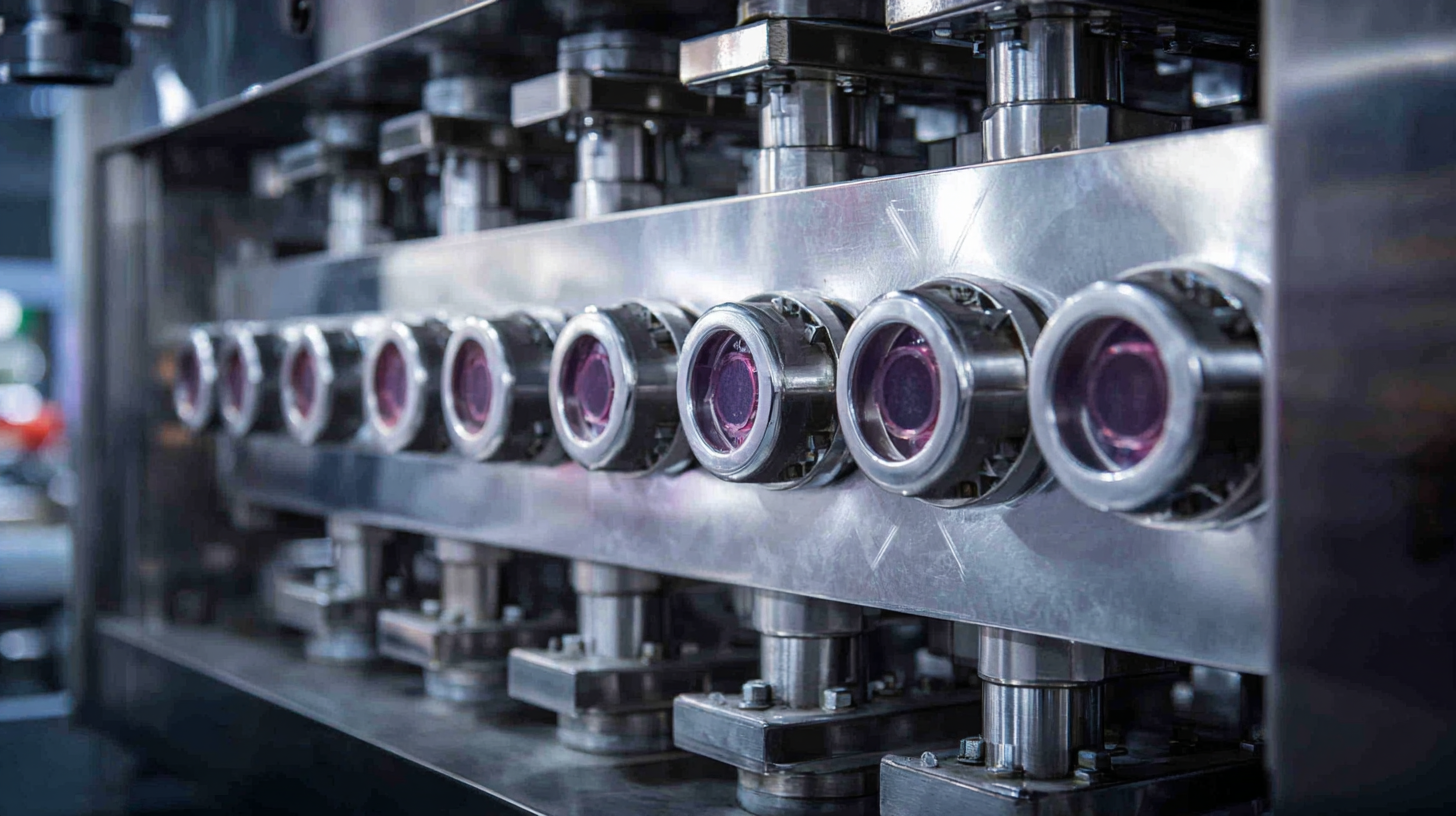

When selecting a plate to plate heat exchanger for your business, several critical factors must be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. First and foremost, consider the thermal requirements of your process. This entails understanding the temperature ranges and the specific heat transfer rates needed to meet operational demands. Different applications may require varying heat exchanger designs, so assessing the thermal load accurately is key to making an informed choice.
Another significant factor is the compatibility of materials. Depending on the nature of the fluids being processed, you may need to choose materials that resist corrosion and fouling, ensuring longevity and reliability. Additionally, the pressure drop across the heat exchanger must be evaluated; higher pressure drops can lead to increased energy costs and may affect system performance.
Finally, consider the ease of maintenance and cleaning, as a heat exchanger that can be easily disassembled and serviced will save your business time and money in the long run. By carefully weighing these factors, you can choose a plate to plate heat exchanger that aligns with your operational needs and enhances your efficiency.
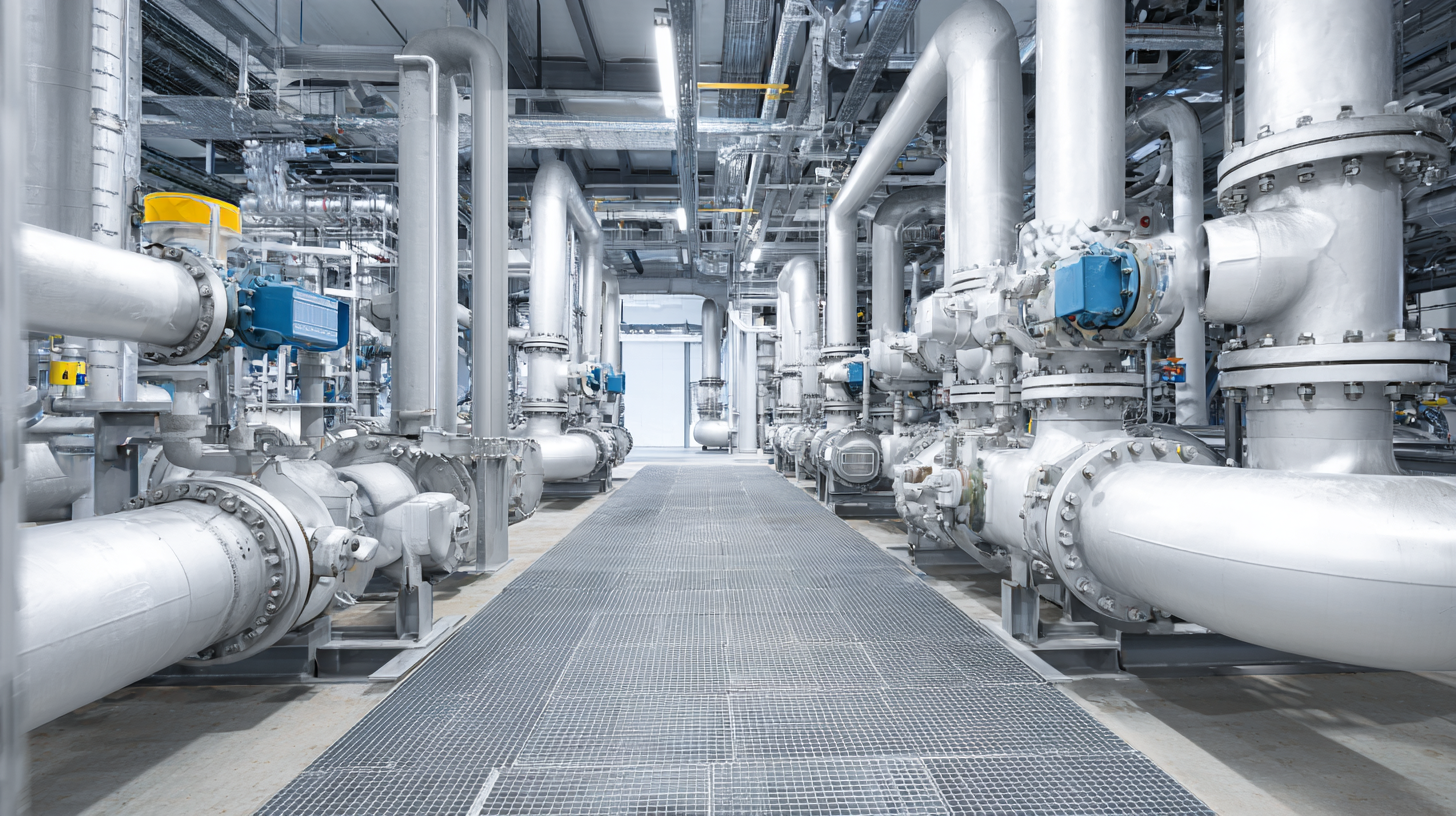

When selecting a plate to plate heat exchanger for your business, avoiding common pitfalls can save both time and money. One prevalent mistake is underestimating the required thermal performance. Many businesses opt for a heat exchanger based on initial cost rather than its efficiency and capacity to handle specific thermal loads. This can lead to performance issues and increased energy consumption, ultimately negating any cost savings.
Another common error is neglecting the maintenance and cleaning requirements of the heat exchanger. Failing to choose a model that is easy to clean or maintain can result in frequent operational downtimes and higher operational costs. It’s crucial to select a unit that offers accessible design for maintenance, ensuring that it remains efficient and prolongs its lifespan.
Lastly, businesses often overlook the importance of compatibility with existing systems. The heat exchanger must not only fit physically within the designated space but also be compatible with the fluids being utilized. Integrating incompatible systems can lead to inefficiencies or even damage to the equipment. Thus, thorough research and careful planning are essential to avoid these mistakes and ensure a successful selection process.
| Parameter | Considerations | Common Mistakes |
|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | Corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity | Choosing materials not compatible with the fluids |
| Heat Transfer Efficiency | Flow arrangement, surface area | Underestimating the need for surface area |
| Pressure Drop | Impact on pumping costs and system efficiency | Ignoring the total system pressure drop |
| Temperature Requirements | Maximum and minimum operating temperatures | Not accounting for temperature variations |
| Maintenance Needs | Access for cleaning and inspections | Overlooking regular maintenance plans |
| Sizing | Flow rates and thermal load calculations | Selecting a unit too small for requirements |
Maintaining your plate to plate heat exchanger is essential for ensuring its longevity and optimal performance.
Regular inspection and cleaning should be at the top of your maintenance checklist. Over time, contaminants can build up within the plates, leading to reduced efficiency and potential system failure.
Establish a routine for checking the system for any signs of corrosion or blockages, as these issues can seriously impact the functionality of the heat exchanger.
Additionally, pay attention to the operating conditions of your heat exchanger. Excessive temperatures and pressures can contribute to premature wear. Monitoring these parameters and making necessary adjustments can prevent costly repairs or replacements down the line.
Implementing a proactive maintenance schedule not only ensures the efficient operation of your heat exchanger but also extends its service life, ultimately benefiting your business operations. Remember, a well-maintained system is key to achieving optimal heat transfer and avoiding unexpected downtimes.






